UBE RID





- Outline
- Features
- Uses
- Basic Principle
- System Configuration
- Processing Capacity
- Indicators
- Safety
- Replacement System
- Warranty Period and System Lifetime
- Treatment Agent
- Equipment Types
- Housing
Outline

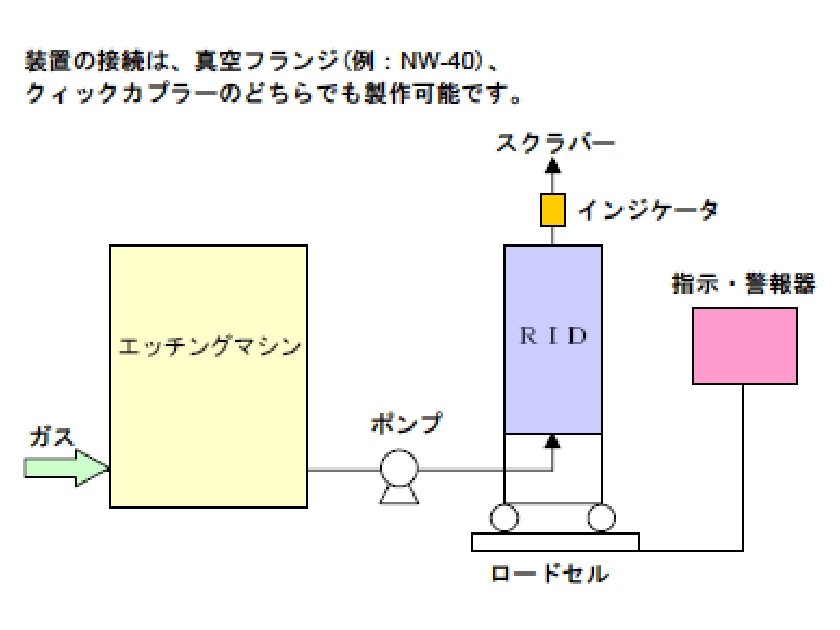
This equipment efficiently renders the various toxic gases emitted during the semiconductor manufacturing process chemically and physically harmless. It includes indicators showing when replacement is necessary. Load cells and gas detectors inform the operator when this is necessary.
*UBE RID is a registered trademark in Japan.
Features
Dry treatment system
There is no clogging because this is a totally dry treatment system.
Improved safety for clients' manufacturing processes
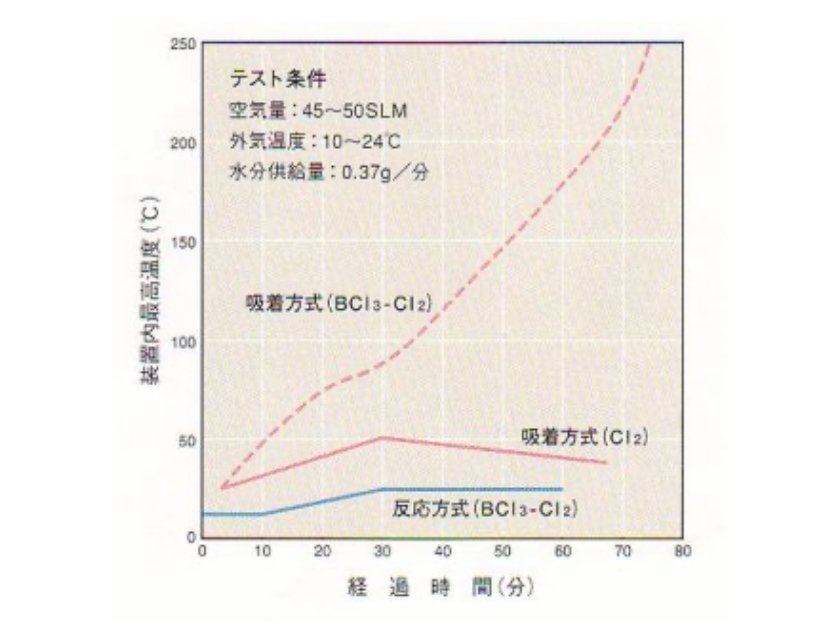
There is no fear of heat release accidents because the gas is chemically treated. . This also makes it safe in the event of traffic accidents while transporting. UBE RID for treating toxic gases using an absorption method is also available separately.
Digital display of treatment volume
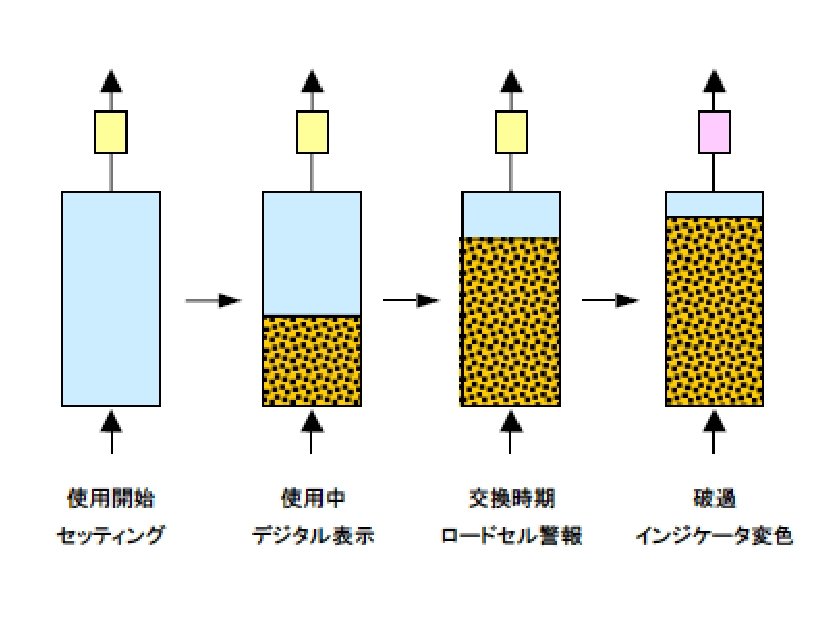
Throughput can be determined at a glance thanks to the load cell, even while using the system, making it easy to decide when replacement is required.
Two-stage warning system for replacement timing
When it is time for replacement, the operator will be informed by an audible alarm and lamp. At the same time, replacement time can be determined using the indicators.
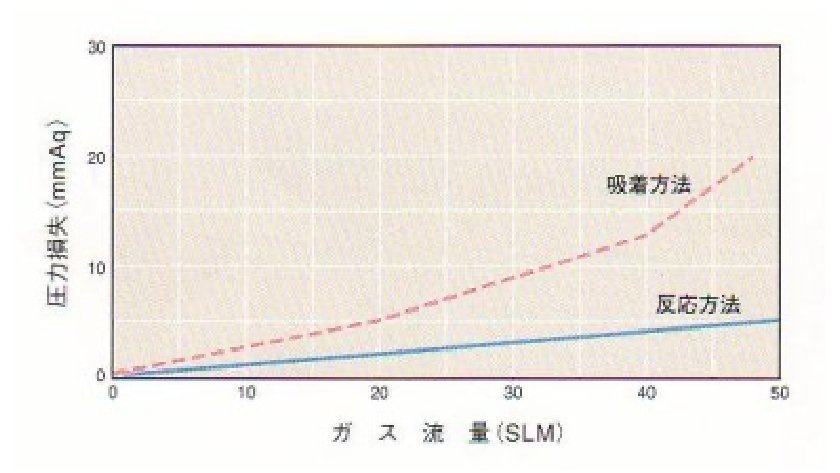
Small pressure loss
No heavy burden is placed on the pump because the system was designed for small-pressure flow.
Simple connection
Gas can be introduced from either the top or bottom depending on the model of the treatment system used, and there is no need for major piping work.
Wide applicability
Target gases include chlorine chemicals, such as BCl3, Cl2, SiCl4, and HCl, bromate chemicals, such as HBr, BBr3, and the byproducts of fluorine gas (HF, SF4, SiF4, and SOF2).
Uses
Detoxification and particle treatment of toxic gases emitted from dry-etching systems and other manufacturing facilities, as well as from cylinder cabinets.
Target Gases
- Chlorine chemicals(HCl、Cl2、BCl3、SiC4 etc.)
- Bromate chemicals(HBr、Br2、BBr3 etc.)
- Byproducts of fluorine gas(HF、SiF4、SF4 etc.)
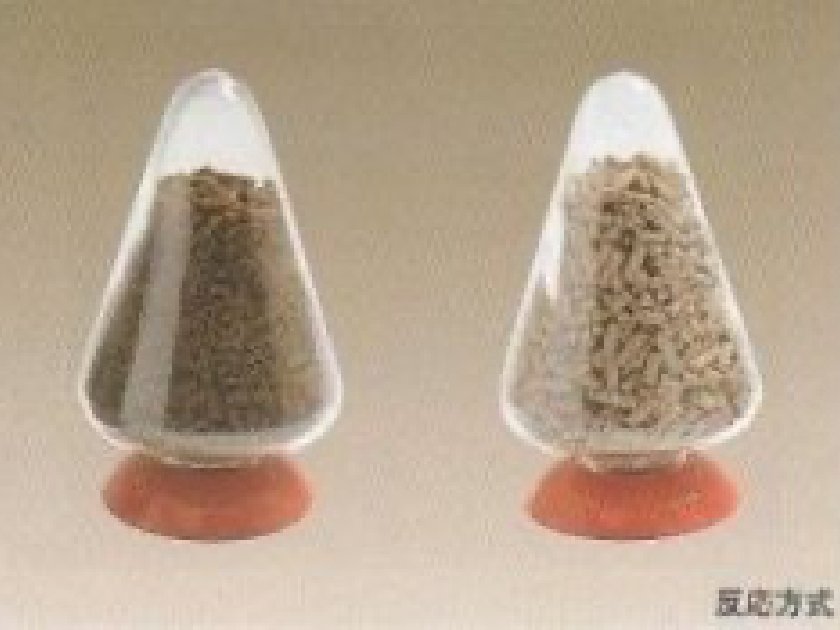
Basic Principle
Reaction method
| Treatment agent |
|
|---|
Adsorption method
| Treatment agent |
|
|---|
System Configuration
Processing Capacity
Reaction method
| Model | BCl3 | HBr |
|---|---|---|
| RID-1,2 | 20kg | 15kg |
| RID-3,4 | 10kg | 8kg |
Adsorption method
| Model | BCl3 | HBr |
|---|---|---|
| RID-1,2 | 13kg | 10kg |
| RID-3,4 | 7kg | 5kg |
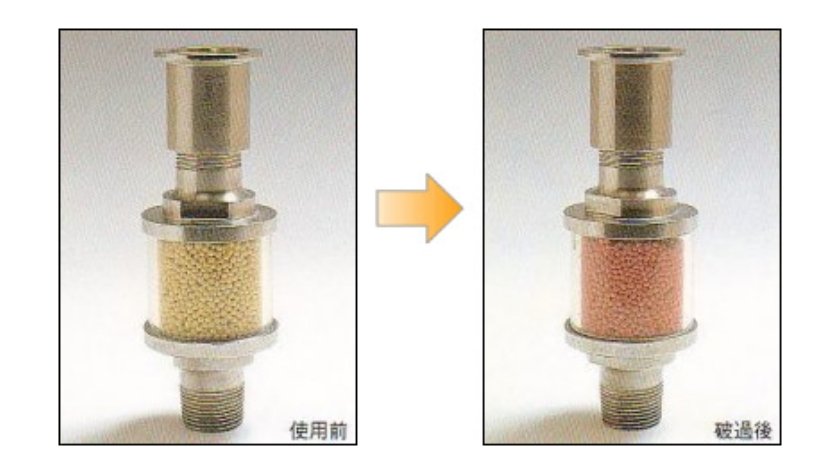
Indicator
1-stage method
Color change by acidic gas

2-stage method
Color change by acidic gas and chlorine
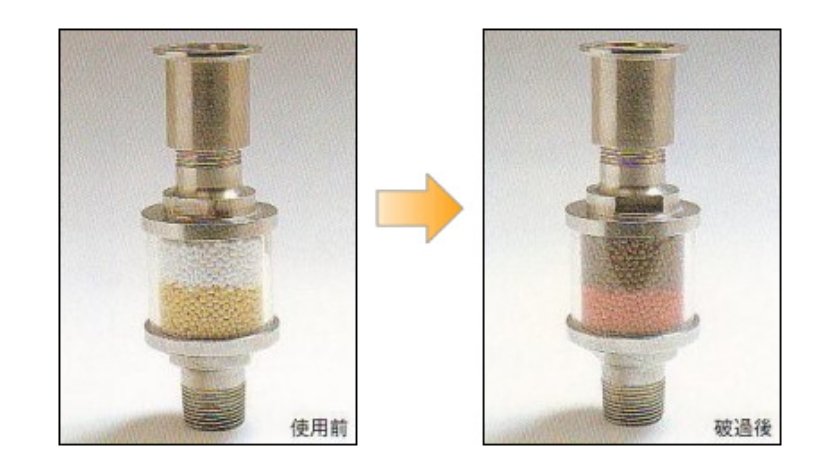

*Indicators change color even under the presence of 0.1ppm gas.
*Color changes other than those shown above may result depending on the type of gas.
When the entire indicator has changed color, consider it a sign that the treatment agent is spent.
Safety
Heat release
Pressure loss
Pressure resistance
This system is not pressure resistant, so do not apply pressures of 0.1kg/cm² or greater.
Replacement System
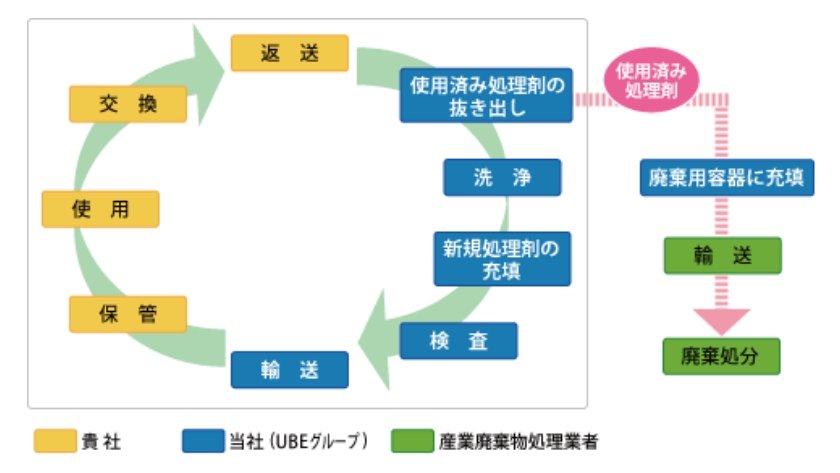
- Even if the treatment agent is not spent, it should be replaced after four months of use for the sake of system longevity and safety.
- A returned system will normally be sent back within three weeks.
- A spent treatment agent is taken and disposed of by a firm licensed to dispose of industrial waste.
- A spent treatment agent is handled as industrial waste once it is removed by UEL, a subsidiary of UBE, eliminating the need for users to deal with troublesome procedures.
Warranty Period and System Lifetime
- The system is expected to last one year.
- The system's lifetime will differ depending on usage. Note that repairs requested for deterioration or rupturing of pipes or other parts due to corrosion are not free of charge.
Treatment Agent
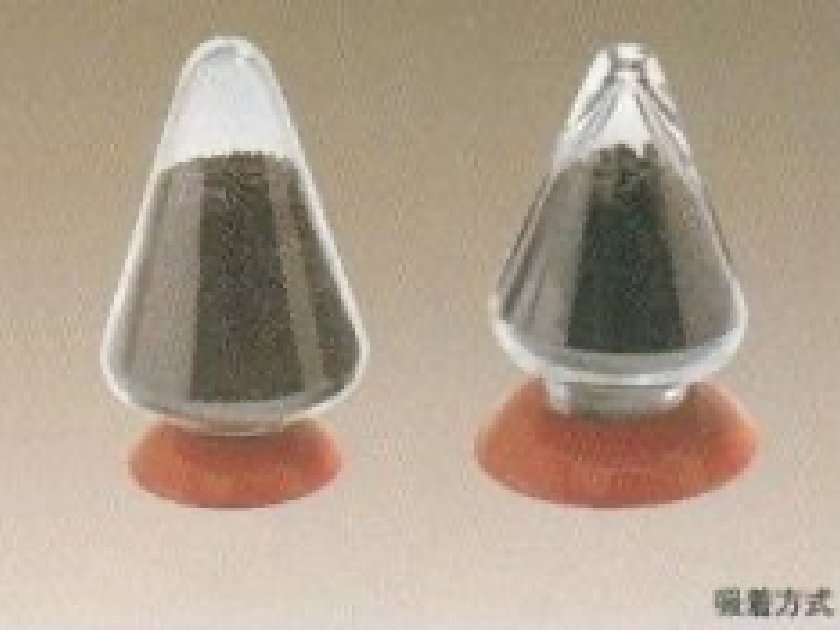


Equipment Types





