2025/11/ 6
2025/11/ 6
UPIA®-NF





About UPIA®-NF
UPIA®-NF is a polyimide precursor under UBE's polyimide varnish brand UPIA®, formulated without the use of the organic solvent NMP (NMP-Free (NF)).
NEWS
 2025/11/ 6
2025/11/ 6
 2025/10/ 1
2025/10/ 1
 2025/3/12
2025/3/12
UPIA®-NF development
Collaboration as a Catalyst for Creation
Creating new value with our customers under the spirit
of "Coexistence and mutual prosperity"
Challenge of developing polyimides
without using organic solvents to
reduce environmental impact
A challenge to achieve material hybridization
previously unattainable
with organic solvents
"help to solve global environmental issues, which have become a common issue for all humankind, and contribute to people's lives and health, and an enriched future society."
"Excerpt ; UBE Purpose"
Overview
-
NMP-free
Water-based varnish -
Approximately
80% reduction
in NMP solvent content -
Environmentally friendly and
improved
workplace safety -
Uses BPDA,manufactured
in-house by UBE,
as a raw material -
Capable of low-temperature
thermal processing:
from 150℃ -
Refrigerated storage
recommended

Features
-
Development Product 1
Parameter
- Solvent
- Water
- Glass Transition
Temperature (Tg) - 145℃
- Elongation at Break
- 199%
- Tensile Elasticity
- 1.9GPa
- Tensile Strength at Break
- 106MPa
- Insulation Breakdown
Voltage - 5.5kV/mm
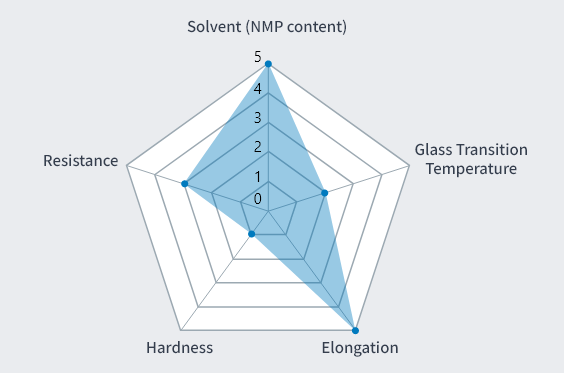
Features
- ・Imidization proceeds well at 150℃.
- ・Excellent elongation; more flexible compared to conventional polyimides.
-
Development Product 2
Parameter
- Solvent
- Water
- Glass Transition
Temperature (Tg) - 210℃
- Elongation at Break
- 164%
- Tensile Elasticity
- 3.2GPa
- Tensile Strength at Break
- 214MPa
- Insulation Breakdown
Voltage - 6.3kV/mm
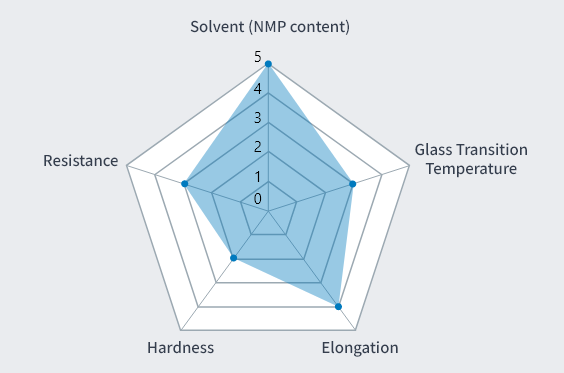
Features
- ・Possesses intermediate properties between Development Products 1 and 2.
-
Development Product 3
Parameter
- Solvent
- Water
- Glass Transition
Temperature (Tg) - 339℃
- Elongation at Break
- 96%
- Tensile Elasticity
- 4.6GPa
- Tensile Strength at Break
- 289MPa
- Insulation Breakdown
Voltage - 6.5kV/mm
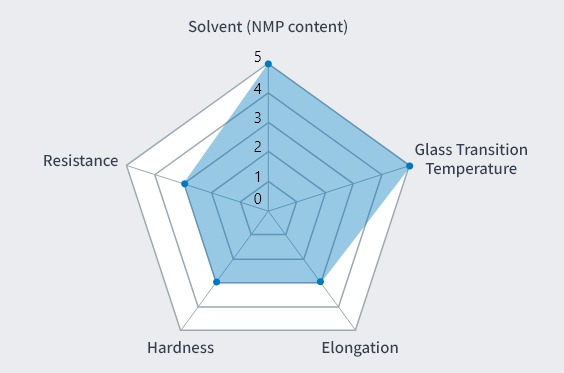
Features
- ・High heat resistance and high tensile elasticity composition. Exhibits properties comparable to conventional polyimides.
Applications
Expected Applications and Uses
Information
Surface resistance of polyimide with dispersed CNT
●Evaluation Content
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) are materials formed by rolling graphene sheets into tubular structures. They possess outstanding properties such as high electrical conductivity, high mechanical strength, and high thermal conductivity.
These characteristics make CNTs promising for a wide range of applications, including conductive materials for electronic components, electromagnetic wave shielding, and heat dissipation sheets etc.
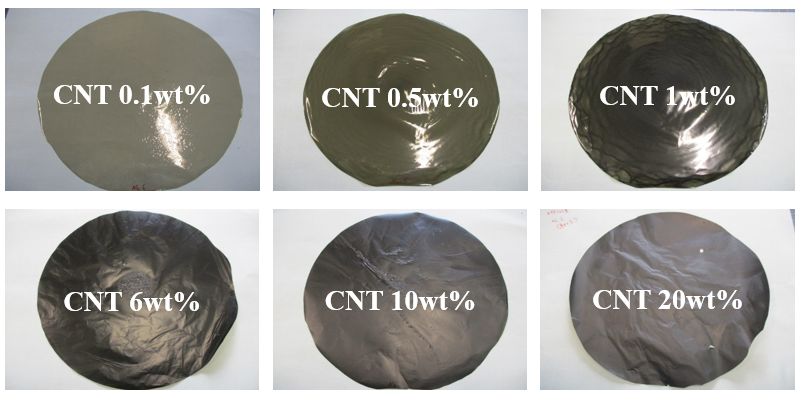
In our experiment, single-walled CNTs were dispersed in a water-solvent polyimide (polyimide precurcer) and formed into a film on a glass substrate. Even with the addition of 20 wt% CNTs, a freestanding film was successfully fabricated.
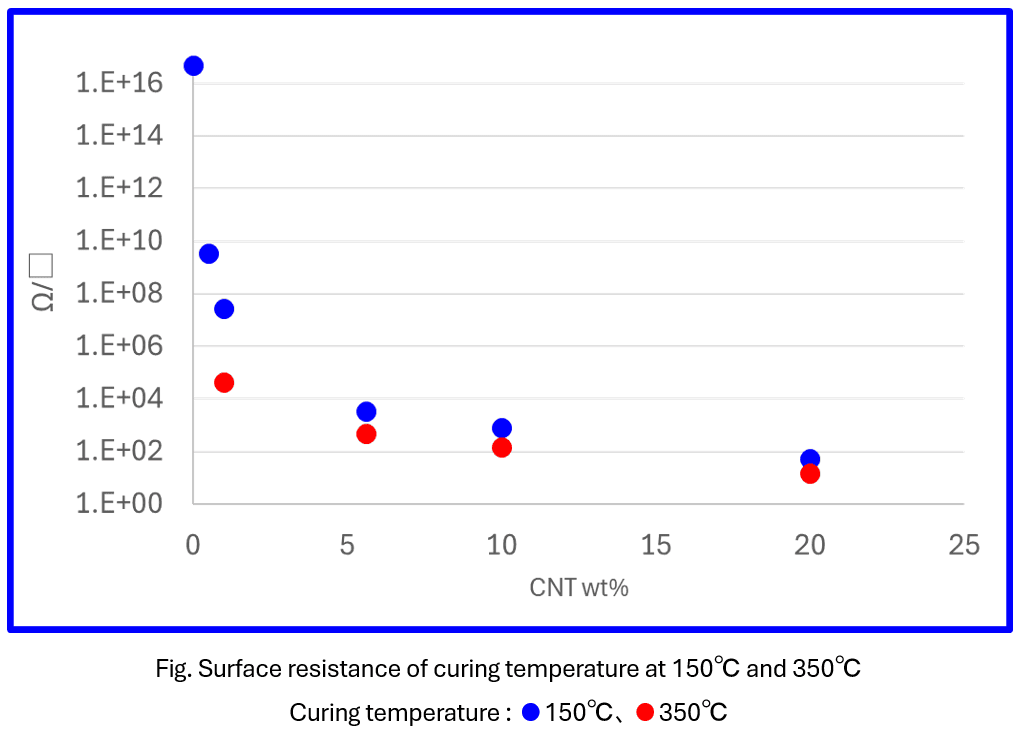
We measured the surface resistance while varying the CNT content and calcination temperature. The results confirmed that increasing the CNT content leads to a decrease in surface resistance, and similarly, raising the heat treatment temperature also results in lower surface resistance.
By using polyimide, we envision applications in high heat-resistant electromagnetic wave shielding and water-soluble heat-resistant coatings etc.
●Film making method
Mixing CNT and Water solvent polyimide
↓
Spin coating on glass
↓
Pre-Cure(40℃ 10min with HVCD)
↓
Post-Cure(150℃ 60min. or 350℃ 30min.)
↓
Detachment(Film thickness :10μm)
●Surface resistance
| Type | Unit | U-Varnish-S | U-Varnish-A | Development Product1 |
Development Product2 |
Development Product3 |
Test Condition Test method |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Film thickness | um | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | ||
| Maximum heat treament temperature |
℃ | 450 | 350 | 150 | 250 | 350 | ||
| solvent | ー | NMP | NMP | Water | Water | Water | ||
| Solid Content | wt% | 18.0±1.0 | 18.0±1.0 | 18 | 11 | 18 | 350℃, 30min | |
| viscosity | Pa・s | 5±1 | 5±1 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 4 | 30℃ | |
| Density | 103kg/m3 | 1.10~1.11 | 1.10~1.11 | ー | ー | 1.10 | 25℃ | |
| Strage condition | ℃ | <30℃ | <30℃ | <30℃ | <30℃ | <30℃ | ||
| Film properties |
glass transition temperature Tg |
℃ | 322 | 274 | 145 | 210 | 339 | Dynamic viscoelasticity |
| Tensile Strength | MPa | 526 | 229 | 106 | 214 | 289 | ASTM D882 | |
| Elongati on | % | 35 | 92 | 199 | 164 | 96 | ASTM D882 | |
| Tensile Elasticity |
GPa | 9.8 | 3.7 | 1.9 | 3.2 | 4.6 | ASTM D882 | |
| 5% Heat Weight Reduction Temperature |
℃ | 619 | 592 | ー | ー | 574 | TGA | |
| Insulation Breakdown Voltage |
kV | 7.0 | 7.7 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 6.5 | ASTM D149 | |